中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 37-46.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00047
收稿日期:2024-12-09
修回日期:2025-03-11
出版日期:2025-11-20
发布日期:2025-11-26
通讯作者:
刘金鹏
作者简介:康红梅(1973—),女,甘肃兰州人,博士,研究方向为生态修复技术。E-mail: lzkanghm@163.com
基金资助:
Hongmei Kang1( ), Jun Zhang1, Xin Li1, Jinpeng Liu2(
), Jun Zhang1, Xin Li1, Jinpeng Liu2( )
)
Received:2024-12-09
Revised:2025-03-11
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-26
Contact:
Jinpeng Liu
摘要:
为探究人工接种复合藻液对河西走廊工程迹地生物结皮(Biological soil crusts, BSC)生长及土壤性质的影响,在甘肃古浪模拟5种工程扰动面(Disturbed surfaces, S),人工喷施复合藻液(Treatments,T),观测不同扰动面和处理下BSC生长和土壤养分等的变化。结果显示:不同的扰动面BSC生长良好,无明显风蚀发生。S对BSC的生长、土壤养分和土壤酶活性影响极其显著(P<0.001);T在短期内对BSC生长影响不明显,但随着时间的延长各扰动面BSC生物量、BSC厚度、土壤养分和土壤磷酸酶显著增加(P<0.05,2 a)。填方边坡阴坡的BSC生长最快(1.629 µg·g-1 Chl a,2 a),比3个月时的BSC生物量增加了439.4%;BSC厚度、土壤酶活性、有效磷及速效钾含量均显著高于其他扰动面(P<0.05)。复合藻液可有效诱导BSC,其土壤硬度、BSC生物量、碱性磷酸酶和土壤养分显著增加(P<0.05)。藻液、微生物菌剂和沙蒿胶的联合固沙新方法可用于工程建设扰动后BSC快速重建。扰动面类型对人工BSC的发育影响显著,阴坡更利于BSC定植和生长。
中图分类号:
康红梅, 张军, 李鑫, 刘金鹏. 接种复合藻液对河西走廊工程扰动面生物结皮及土壤性质的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(6): 37-46.
Hongmei Kang, Jun Zhang, Xin Li, Jinpeng Liu. Effects of artificially inoculated composite algal solutions on biological soil crusts and soil properties in engineering-disturbed areas of the Hexi Corridor[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(6): 37-46.
| 参数 | 扰动面S(n=12) | 处理T(n=15) | S×T | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | |||
| dF | 4 | 3 | 12 | |||||
| SWC | 97.176*** | 1.293ns | 1.926ns | 0.773ns | 0.875ns | 0.616ns | ||
| pH | 7.667*** | 17.244*** | 0.658ns | 0.446ns | 3.328** | 2.313* | ||
| 土壤硬度 | 6.576*** | 3.285* | 0.978ns | 5.171** | 2.713** | 1.736ns | ||
| 叶绿素a | 10.429*** | 9.103*** | 2.224ns | 8.166*** | 1.686ns | 2.902** | ||
| BSC厚度 | 3.194* | 24.807*** | 0.282ns | 2.934* | 1.362ns | 1.028ns | ||
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 13.909*** | 18.557*** | 2.563ns | 4.125* | 2.670** | 2.218* | ||
| 脲酶 | 20.290*** | 36.330*** | 0.708ns | 1.641ns | 2.948** | 1.565ns | ||
| 过氧化氢酶 | 16.405*** | 24.832*** | 1.684ns | 2.355ns | 2.942** | 2.371* | ||
| 有机质 | — | 26.315*** | — | 1.942ns | — | 2.175* | ||
| 全氮 | — | 10.798*** | — | 1.742ns | — | 3.282** | ||
| 有效磷 | — | 45.868*** | — | 3.153* | — | 5.045*** | ||
| 速效钾 | — | 15.389*** | — | 3.403* | — | 1.108ns | ||
表1 BSC及土壤理化参数对不同扰动面(Disturbed surfaces,S)和处理(Treatments,T)的双因素方差分析结果( F )
Table 1 Results of two-way ANOVA comparing the effects of disturbed surfaces (S) and treatments (T) on BSC and soil physicochemical parameters
| 参数 | 扰动面S(n=12) | 处理T(n=15) | S×T | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | |||
| dF | 4 | 3 | 12 | |||||
| SWC | 97.176*** | 1.293ns | 1.926ns | 0.773ns | 0.875ns | 0.616ns | ||
| pH | 7.667*** | 17.244*** | 0.658ns | 0.446ns | 3.328** | 2.313* | ||
| 土壤硬度 | 6.576*** | 3.285* | 0.978ns | 5.171** | 2.713** | 1.736ns | ||
| 叶绿素a | 10.429*** | 9.103*** | 2.224ns | 8.166*** | 1.686ns | 2.902** | ||
| BSC厚度 | 3.194* | 24.807*** | 0.282ns | 2.934* | 1.362ns | 1.028ns | ||
| 碱性磷酸酶 | 13.909*** | 18.557*** | 2.563ns | 4.125* | 2.670** | 2.218* | ||
| 脲酶 | 20.290*** | 36.330*** | 0.708ns | 1.641ns | 2.948** | 1.565ns | ||
| 过氧化氢酶 | 16.405*** | 24.832*** | 1.684ns | 2.355ns | 2.942** | 2.371* | ||
| 有机质 | — | 26.315*** | — | 1.942ns | — | 2.175* | ||
| 全氮 | — | 10.798*** | — | 1.742ns | — | 3.282** | ||
| 有效磷 | — | 45.868*** | — | 3.153* | — | 5.045*** | ||
| 速效钾 | — | 15.389*** | — | 3.403* | — | 1.108ns | ||
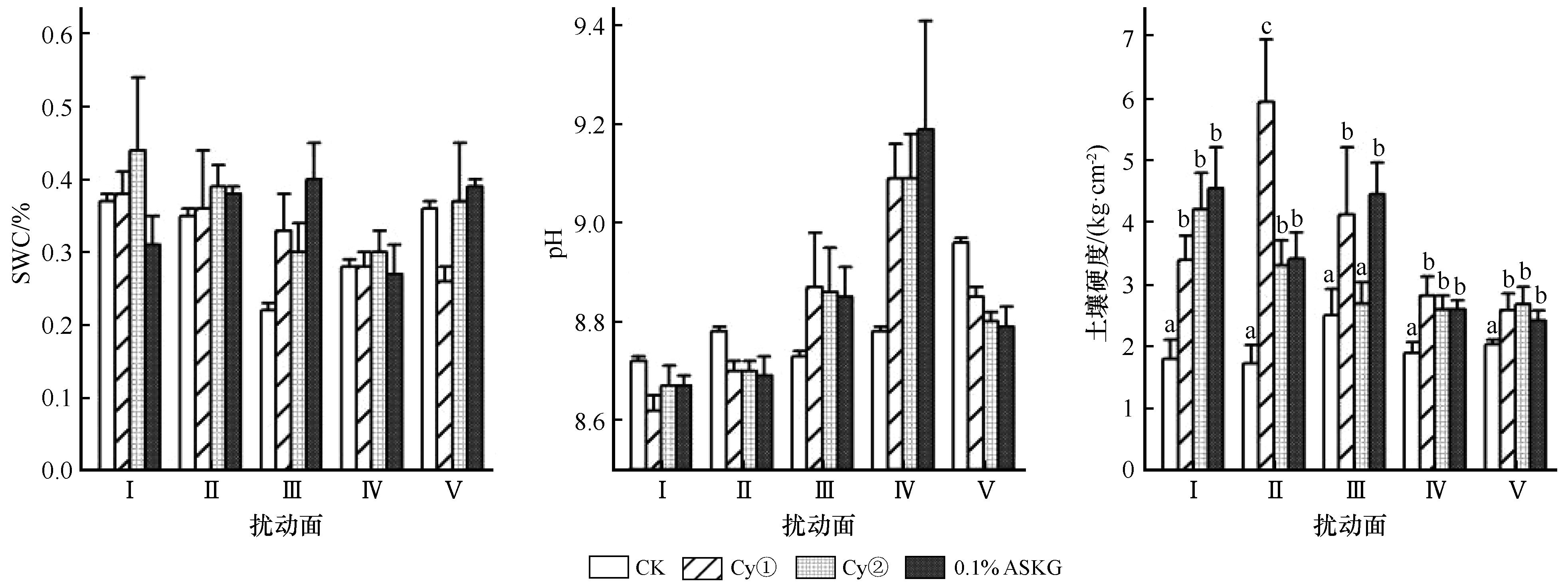
图1 2 a时不同扰动面(S)及处理(T)下的SWC、pH值及土壤硬度注:不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异性显著
Fig.1 SWC, pH, and soil hardness across different disturbed surfaces (S) and treatments (T) after 2 years of inoculation
| 扰动面 | pH | 土壤硬度/(kg·cm-2) | Chl a/(μg·g-1) | BSC厚度/mm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | ||||
| Ⅰ | 8.24±0.02b | 8.67±0.01a | 1.94±0.23c | 3.82±0.31b | 0.56±0.06ab | 0.93±0.07ab | 0.67±0.03bc | 2.18±0.10a | |||
| Ⅱ | 8.23±0.01b | 8.72±0.15a | 1.58±0.14b | 3.97±0.42b | 0.33±0.05a | 0.68±0.12a | 0.68±0.04c | 2.68±0.12b | |||
| Ⅲ | 8.20±0.01b | 8.83±0.04b | 1.46±0.13b | 3.63±0.39b | 0.91±0.12c | 1.21±0.12bc | 0.60±0.03ab | 3.46±0.13c | |||
| Ⅳ | 8.15±0.02a | 9.04±0.07c | 0.73±0.07a | 2.59±0.12a | 0.30±0.05a | 1.63±0.31c | 0.62±0.02ab | 4.02±0.15d | |||
| Ⅴ | 8.23±0.01b | 8.85±0.02b | 1.50±0.08b | 2.50±0.14a | 0.71±0.12bc | 1.35±0.13bc | 0.54±0.01a | 3.71±0.17cd | |||
表2 不同扰动面(S)的pH值、土壤硬度及BSC生长情况
Table 2 pH, soil hardness, and BSC growth under different disturbed surfaces
| 扰动面 | pH | 土壤硬度/(kg·cm-2) | Chl a/(μg·g-1) | BSC厚度/mm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | ||||
| Ⅰ | 8.24±0.02b | 8.67±0.01a | 1.94±0.23c | 3.82±0.31b | 0.56±0.06ab | 0.93±0.07ab | 0.67±0.03bc | 2.18±0.10a | |||
| Ⅱ | 8.23±0.01b | 8.72±0.15a | 1.58±0.14b | 3.97±0.42b | 0.33±0.05a | 0.68±0.12a | 0.68±0.04c | 2.68±0.12b | |||
| Ⅲ | 8.20±0.01b | 8.83±0.04b | 1.46±0.13b | 3.63±0.39b | 0.91±0.12c | 1.21±0.12bc | 0.60±0.03ab | 3.46±0.13c | |||
| Ⅳ | 8.15±0.02a | 9.04±0.07c | 0.73±0.07a | 2.59±0.12a | 0.30±0.05a | 1.63±0.31c | 0.62±0.02ab | 4.02±0.15d | |||
| Ⅴ | 8.23±0.01b | 8.85±0.02b | 1.50±0.08b | 2.50±0.14a | 0.71±0.12bc | 1.35±0.13bc | 0.54±0.01a | 3.71±0.17cd | |||
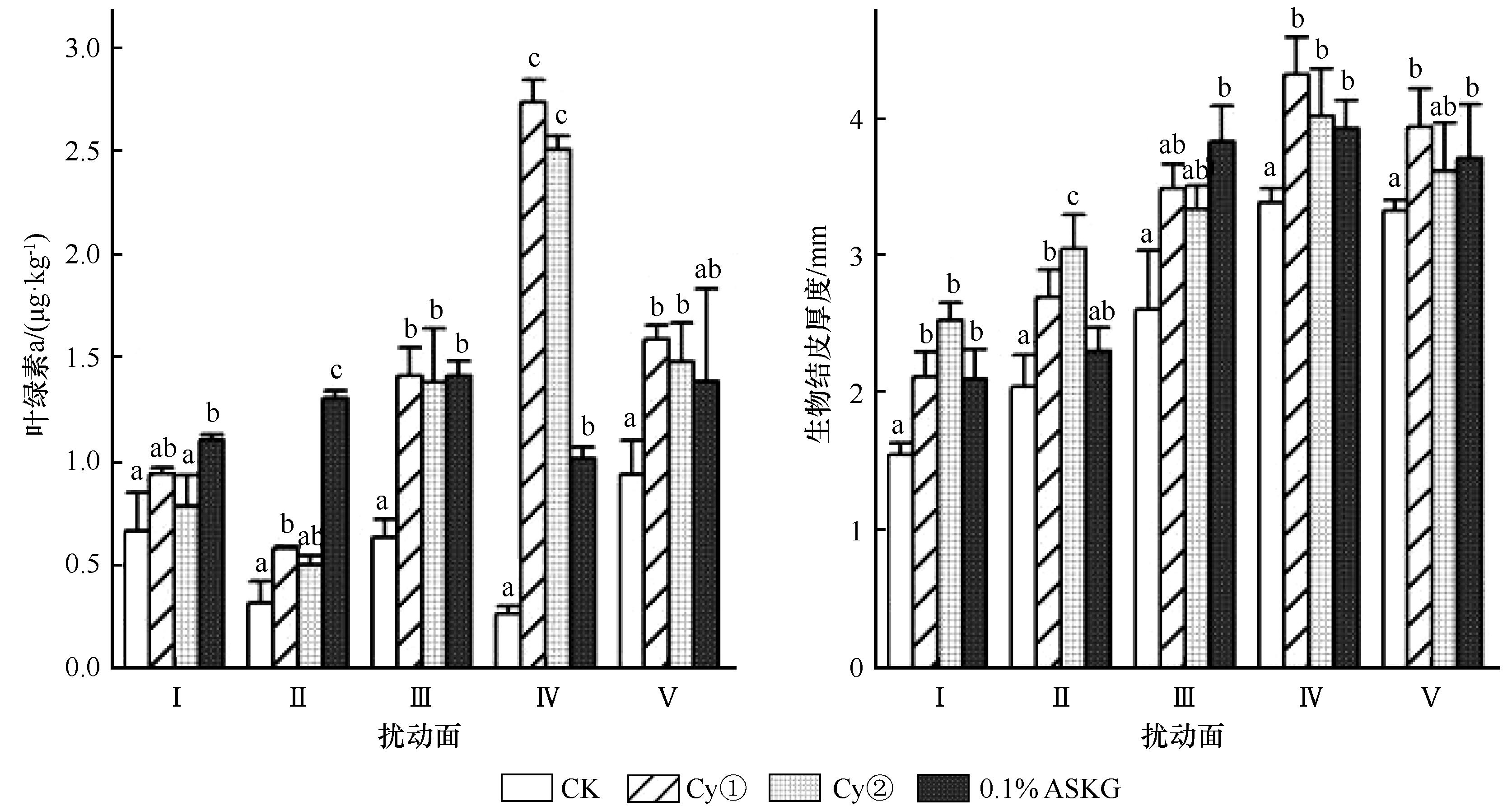
图2 2 a时不同扰动面(S)及处理(T)下的BSC生长情况注:不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异性显著
Fig.2 The growth of BSC across different disturbed surfaces (S) and treatments (T) after 2 years of inoculation
| 扰动面 | 碱性磷酸酶/(μg·g-1-24h) | 脲酶(NH3-N μg·g-1-24h) | 过氧化氢酶/(mL·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | |||
| Ⅰ | 20.71±2.04a | 38.78±3.84a | 0.56±0.05a | 1.19±0.05a | 0.61±0.01a | 0.66±0.01a | ||
| Ⅱ | 38.65±2.27b | 42.53±3.66ab | 0.86±0.07b | 2.00±0.06b | 0.69±0.01c | 0.69±0.02b | ||
| Ⅲ | 41.56±6.31bc | 53.6±9.05b | 1.05±0.07c | 2.13±0.15bc | 0.69±0.01c | 0.71±0.01b | ||
| Ⅳ | 51.93±4.07c | 80.5±4.01c | 1.02±0.09c | 2.85±0.17d | 0.63±0.01ab | 0.77±0.01c | ||
| Ⅴ | 48.63±3.37bc | 73.12±3.88c | 1.27±0.05d | 2.40±0.04c | 0.65±0.01b | 0.76±0.01c | ||
表3 不同扰动面(S)的土壤酶活性
Table 3 Soil enzyme activities at different disturbed surfaces (S)
| 扰动面 | 碱性磷酸酶/(μg·g-1-24h) | 脲酶(NH3-N μg·g-1-24h) | 过氧化氢酶/(mL·g-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | 3个月 | 2 a | |||
| Ⅰ | 20.71±2.04a | 38.78±3.84a | 0.56±0.05a | 1.19±0.05a | 0.61±0.01a | 0.66±0.01a | ||
| Ⅱ | 38.65±2.27b | 42.53±3.66ab | 0.86±0.07b | 2.00±0.06b | 0.69±0.01c | 0.69±0.02b | ||
| Ⅲ | 41.56±6.31bc | 53.6±9.05b | 1.05±0.07c | 2.13±0.15bc | 0.69±0.01c | 0.71±0.01b | ||
| Ⅳ | 51.93±4.07c | 80.5±4.01c | 1.02±0.09c | 2.85±0.17d | 0.63±0.01ab | 0.77±0.01c | ||
| Ⅴ | 48.63±3.37bc | 73.12±3.88c | 1.27±0.05d | 2.40±0.04c | 0.65±0.01b | 0.76±0.01c | ||
| 扰动面 | 有机质/(g·kg-1) | 全N /(g·kg-1) | 有效P/(mg·kg-1) | 速效K/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 6.78±0.38b | 1.82±0.35a | 5.75±0.40b | 114.25±7.24a |
| Ⅱ | 7.48±0.11b | 4.71±0.71b | 9.43±0.60c | 142.25±7.04a |
| Ⅲ | 7.14±0.26b | 4.77±0.51b | 4.35±0.21a | 156.20±28.49a |
| Ⅳ | 6.73±0.35b | 2.56±0.41a | 11.35±0.95d | 304.00±37.12b |
| Ⅴ | 4.31±0.16a | 2.80±0.46a | 6.88±0.51b | 117.35±5.31a |
表4 2 a时不同扰动面(S)的土壤养分状况
Table 4 Soil nutrient under different disturbed surfaces (S) after 2 years of inoculation
| 扰动面 | 有机质/(g·kg-1) | 全N /(g·kg-1) | 有效P/(mg·kg-1) | 速效K/(mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 6.78±0.38b | 1.82±0.35a | 5.75±0.40b | 114.25±7.24a |
| Ⅱ | 7.48±0.11b | 4.71±0.71b | 9.43±0.60c | 142.25±7.04a |
| Ⅲ | 7.14±0.26b | 4.77±0.51b | 4.35±0.21a | 156.20±28.49a |
| Ⅳ | 6.73±0.35b | 2.56±0.41a | 11.35±0.95d | 304.00±37.12b |
| Ⅴ | 4.31±0.16a | 2.80±0.46a | 6.88±0.51b | 117.35±5.31a |
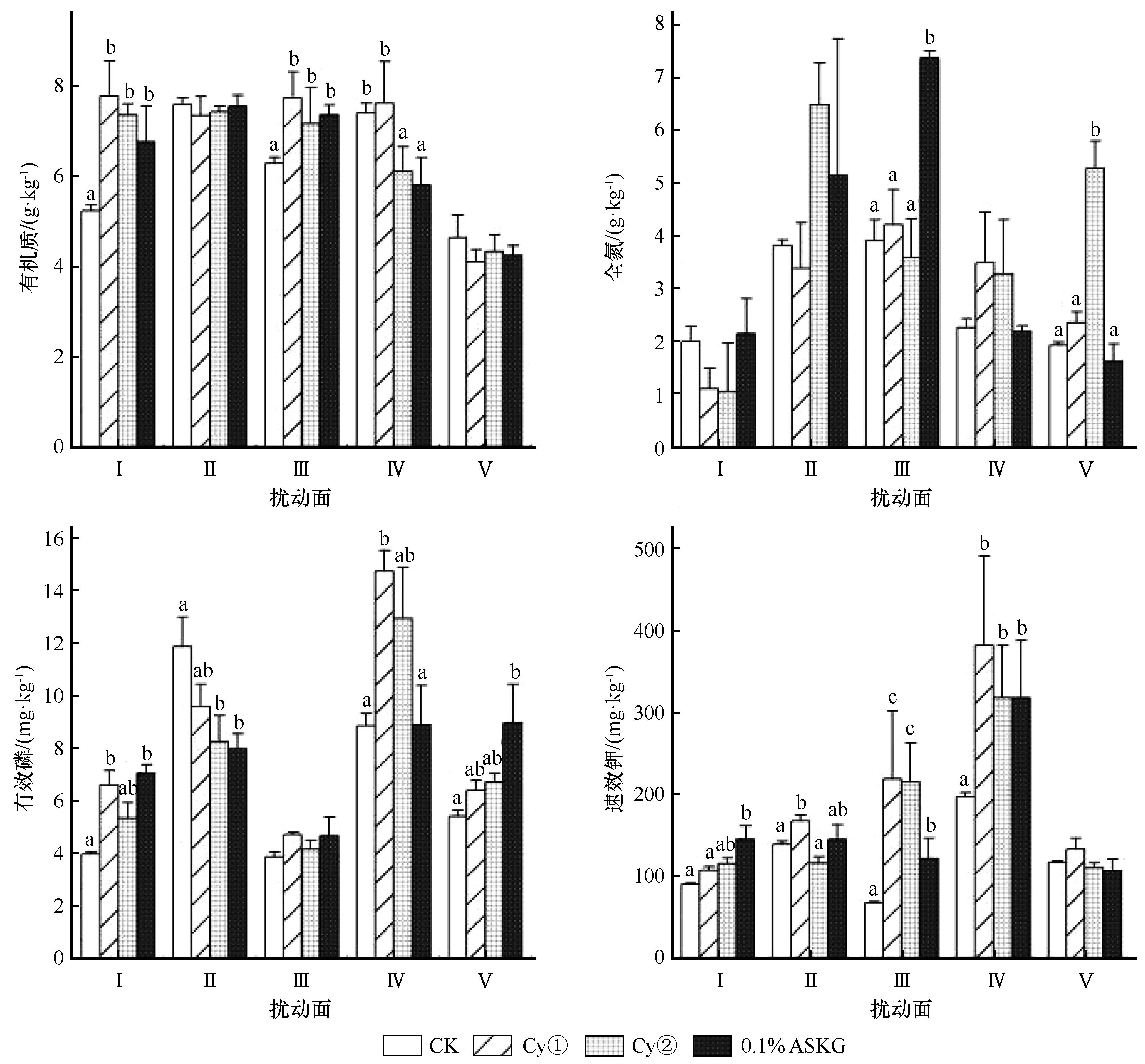
图4 2 a时不同扰动面(S)及处理(T)下的土壤养分注:不同小写字母表示在0.05水平差异性显著
Fig.4 Soil nutrients under different disturbed surfaces (S) and treatments (T) after 2 years of inoculation
| 处理 | 土壤硬度/(kg·cm-2) | Chl a/(μg·g-1) | BSC厚度 /mm | 碱性磷酸酶/(μg·g-1-24h) | 有效P/(mg·kg-1) | 速效K/(mg·kg-1) | H 指数 (扰动面Ⅴ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1(CK) | 1.99±0.38a | 0.702±0.101a | 2.71±0.19a | 47.35±5.97a | 6.79±0.85a | 122.27±11.99a | 1.59±0.13 |
| 2 | 3.67±0.23b | 1.319±0.123b | 3.32±0.11b | 60.60±6.31b | 8.41±0.97b | 201.80±35.08b | 1.80±0.27 |
| 3 | 3.10±0.22b | 1.345±0.170b | 3.31±0.13b | 57.05±4.78ab | 7.49±0.90ab | 175.53±25.64ab | 2.06±0.26 |
| 4 | 3.48±0.23b | 1.345±0.209b | 3.18±0.12b | 65.82±7.01b | 7.52±0.58ab | 167.54±24.68ab | 1.84±0.12 |
表5 2 a时不同处理(T)下BSC生长、土壤性质及生物多样性指数
Table 5 BSC, soil properties and biodiversity index of H under different treatments (T) after 2 years of inoculation
| 处理 | 土壤硬度/(kg·cm-2) | Chl a/(μg·g-1) | BSC厚度 /mm | 碱性磷酸酶/(μg·g-1-24h) | 有效P/(mg·kg-1) | 速效K/(mg·kg-1) | H 指数 (扰动面Ⅴ) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1(CK) | 1.99±0.38a | 0.702±0.101a | 2.71±0.19a | 47.35±5.97a | 6.79±0.85a | 122.27±11.99a | 1.59±0.13 |
| 2 | 3.67±0.23b | 1.319±0.123b | 3.32±0.11b | 60.60±6.31b | 8.41±0.97b | 201.80±35.08b | 1.80±0.27 |
| 3 | 3.10±0.22b | 1.345±0.170b | 3.31±0.13b | 57.05±4.78ab | 7.49±0.90ab | 175.53±25.64ab | 2.06±0.26 |
| 4 | 3.48±0.23b | 1.345±0.209b | 3.18±0.12b | 65.82±7.01b | 7.52±0.58ab | 167.54±24.68ab | 1.84±0.12 |
| [1] | 田玉清,石道良,张淑倩,等.河西走廊水生植物多样性格局,群落特征及影响因素[J].生态学报,2020,40(1):202-212. |
| [2] | Rossi F, Li H, Liu Y D,et al.Cyanobacterial inoculation (cyanobacterisation): perspective for the development of a standardized multifunctional technology for soil fertilization and desertification reversal[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2017,171:28-43. |
| [3] | Zhou X J, Ke T, Li Sh X,et al.Induced biological soil crusts and soil properties varied between slope aspect,slope gradient and plant canopy in the Hobq Desert of China[J].Catena,2020,190:104559. |
| [4] | 周香君.人工生物土壤结皮的形成发育及其对微生境的响应机制[D].武汉:武汉大学,2019. |
| [5] | West N E.Structure and function of microphytic soil crusts in wildland ecosystems of arid to semi-arid regions[J].Advances in Ecological Research,1990,20:179-223. |
| [6] | Eldridge D J, Greene R S B.Microbiotic soil crusts: a review of their roles in soil and ecological processes in the rangelands of Australia[J].Australian Journal of Soil Research,1994,32:389-415. |
| [7] | 李新荣,谭会娟,回嵘,等.中国荒漠与沙地生物土壤结皮研究[J].科学通报,2018,63:2320-2334. |
| [8] | Li X R, Xiao H L, Zhang J G,et al.Long-term ecosystem effects of sand-binding vegetation in the Tengger Desert,northern China[J].Restoration Ecology,2004,12:376-390. |
| [9] | Guo Y R, Zhao H L, Zuo X A,et al.Biological soil crust development and its topsoil properties in the process of dune stabilization,Inner Mongolia,China[J].Environmental Geology,2008,54:653-662. |
| [10] | Zhao H L, Guo Y R, Zhou R L,et al.The effects of plantation development on biological soil crust and topsoil properties in a desert in northern China[J].Geoderma,2011,160:367-372. |
| [11] | Xiao B, Zhao Y G, Wang H F,et al.Natural recovery of moss-dominated biological soil crusts after surface soil removal and their long-term effects on soil water conditions in a semiarid environment[J].Catena,2014,120:1-11. |
| [12] | 赵洋,潘颜霞,苏洁琼,等.中国干旱区沙化土地绿色环保治理技术综述[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(1):195-202. |
| [13] | 王楠,许文文,赵燕翘,等.荒漠蓝藻规模化培养试验[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):181-189. |
| [14] | 郑娇莉,李双双,彭成荣,等.干燥对人工生物土壤结皮固氮酶活性恢复过程的影响[J].中国科学:生命科学,2017,47(7):759-769. |
| [15] | 许文文,赵燕翘,王楠,等.人工生物土壤结皮对草本植物群落组成与多样性的影响[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(5):204-211. |
| [16] | 谢作明.荒漠藻类对紫外辐射的响应及其结皮形成的研究[D].武汉:中国科学院水生生物研究所,2006. |
| [17] | 李玉领.沙蒿胶-微藻联合固沙效果的试验[D].湖南衡阳:南华大学,2017. |
| [18] | 张丙昌,王敬竹,张元明,等.水分对具鞘微鞘藻构建人工藻结皮的作用[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(2):535-540. |
| [19] | Wintermans J F, A De Mots.Spectrophotometric characteristics of chlorophylls a and b and their phenophytins in ethanol[J].Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,1965,109(2):448-453. |
| [20] | 关松荫.土壤酶及其研究方法[M].北京:农业出版社,1986:260-342. |
| [21] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000. |
| [22] | 赵允格,许明祥, Jayne B.生物结皮光合作用对光温水的响应及其对结皮空间分布格局的解译:以黄土丘陵区为例[J].生态学报,2010,30(17):4668-4675. |
| [23] | Ai Z, He L R, Xin Q,et al.Slope aspect affects the nonstructural carbohydrates and C∶N∶P stoichiometry of Artemisia sacrorum on the Loess Plateau in China[J].Catena,2017,152:9-17. |
| [24] | Zhang B C, Zhang Y M, Su Y G,et al.Responses of microalgal-microbial biomass and enzyme activities of biological soil crusts to moisture and inoculated Microcoleus vaginatus gradients[J].Arid Land Research and Management,2013,27:216-230. |
| [25] | Wang W B, Liu Y D, Li D H,et al.Feasibility of cyanobacterial inoculation for biological soil crusts formation in desert area[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2008,41:926-929. |
| [26] | Park C H, Li X R, Zhao Y,et al.Rapid development of cyanobacterial crust in the field for combating desertification[J].PLoS ONE,2017,12(6):e0179903. |
| [27] | Xu Y H, Rossi F, Colica G,et al.Use of cyanobacterial polysaccharides to promote shrub performances in desert soils: a potential approach for the restoration of desertified areas[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2012,49:143-152. |
| [28] | Zhao Y M, Zhu Q K, Li P,et al.Effects of artificially cultivated biological soil crusts on soil nutrients and biological activities in the Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Arid Land,2014,6:742-752. |
| [29] | Xiao B, Wang Q H, Zhao Y G,et al.Artificial culture of biological soil crusts and its effects on overland flow and infiltration under simulated rainfall[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2011,48:11-17. |
| [30] | Xiao B, Zhao Y G, Wang Q H,et al.Development of artificial moss-dominated biological soil crusts and their effects on runoff and soil water content in a semi-arid environment[J].Journal of Arid Environment,2015,117:75-83 |
| [31] | Lan S B, Zhang Q Y, Wu L,et al.Artificially accelerating the reversal of desertification: cyanobacterial inoculation facilitates the succession of vegetation communities[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2014,48:307-315. |
| [32] | Guo Q B, Cui S W, Wang Q,et al.Extraction,fractionation and physicochemical characterization of water-soluble polysaccharides from Artemisia sphaerocephala Krasch seed[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,86(2):831-836. |
| [33] | 刘军,张宇清,秦树高,等.不同喷洒浓度沙蒿胶固沙效果试验[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(5):149-155. |
| [34] | 杜宇佳,高广磊,陈丽华,等.土壤微生物膜对风沙土固沙保水特性的影响[J].农业工程学报,2020,36(17):98-105. |
| [35] | Castillo-Monroy A P, Bowker M A, Maestre F T,et al.Relationships between biological soil crusts,bacterial diversity and abundance,and ecosystem functioning:insights from a semi-arid Mediterranean environment[J].Journal of Vegetation Science,2011,22(1):165-174. |
| [36] | 吴玮婷,刘振婷,高广磊,等.枯草芽孢杆菌对沙生植物种子萌发和幼苗生长生理特征的影响[J].中国水土保持科学(中英文),2024,22(6):70-76. |
| [37] | 安富博,张德魁,赵锦梅,等.河西走廊不同类型戈壁土壤理化性质分析[J].中国水土保持,2019,6:42-47. |
| [38] | 谢作明,陈兰洲,李敦海,等.土壤丝状蓝藻在荒漠治理中的作用研究[J].水生生物学报,2007,31(6):886-890. |
| [39] | 陈兰周,刘永定,李敦海,等.荒漠藻类及其结皮的研究[J].中国科学基金,2003,2:90-93. |
| [40] | Barbero-Sierra C, Marques M J, Ruiz-Pérez M,et al.How is desertification research addressed in Spain? land versus soil approaches[J].Land Degradation & Development,2015,26(5):423-432. |
| [1] | 曹怡帆, 王德金, 杨竟艺, 何金凯, 陈静, 赵臣婷. 河西走廊中部荒漠砾幂优先流特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(6): 220-230. |
| [2] | 钟凌飞, 刘鹄, 张丽华. 河西走廊荒漠植被归一化指数(NDVI)与降水量的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 318-327. |
| [3] | 武雅琳, 赵学勇, 张蕊. 沙质草地3种植物群落土壤有机碳氮密度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 357-367. |
| [4] | 陈晶亮, 谭松伟, 刘超, 黄磊. 宁夏罗山典型林分土壤养分特征与凋落物质量的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 326-336. |
| [5] | 隋文舒, 陈颢, 肖锋军, 胡光印, 董治宝. 河西走廊流水型遗迹沙丘的辨识特征与形成模式[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 75-84. |
| [6] | 李军, 周发元, 焦亮, 李开明, 李超灿. 1960—2022年河西走廊主要气候要素特征及气候生产潜力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 14-25. |
| [7] | 邢瑜, 柳本立, 马涛, 王伊蒙. 2000—2023年河西走廊-塔克拉玛干沙漠边缘阻击战核心区风蚀起尘量变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 330-341. |
| [8] | 任珩, 赵文智, 杨荣, 杜泽玉. 河西走廊绿洲农业水生产力提升的途径与对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 217-224. |
| [9] | 赵一丹, 陈拓, 刘阳, 张璐, 张怡洋, 张威, 章高森. 河西荒漠区石下生蓝藻叶绿素荧光参数的日变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 23-28. |
| [10] | 王帅, 马登科, 何志斌, 孙玮皓, 杜军, 李睿, 王文, 杨淑萍, 赵书玄. 宁夏河东沙地植被多样性与土壤的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 202-211. |
| [11] | 冯益明, 卢琦, 姚斌, 席磊, 曹晓明, 刘永萍, 宁虎森. 河西走廊-塔克拉玛干沙漠边缘阻击战核心区现状、区划及任务[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 91-101. |
| [12] | 王伊蒙, 范亚秋, 龙川, 柳本立. 基于文献记录的敦煌地区历史时期沙尘天气序列重建[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 162-171. |
| [13] | 王进, 刘钊, 张玉杰, 濮超, 吴尧, 鄂利锋, 谢全刚. 河西走廊泡果白刺( Nitraria sphaerocarpa )种子表型差异及休眠破除[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 86-95. |
| [14] | 吕王亦庄, 赵文智. 河西走廊酒泉绿洲农田防护林格局与结构[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 237-245. |
| [15] | 李昕阳, 石培基, 尹君锋, 李雅丽, 才文顺. 河西走廊旅游流网络结构特征与优化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 135-145. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
